- Home
- About
- Services
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- Scleroderma
- Musculoskeletal Pain Disorders
- Osteoporosis, Gout, Back Pain
- Myositis, Fibromyalgia
- Tendonitis, Vasculitis, Vasculitis Ulcers
- Infectious Arthritis like Chikungunya
- Joint Pain & Inflammation
- Spondyloarthropathies (AS) & (PsA)
- Other autoimmune diseases
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Contact
- Menu Item
Call us at:
98473 84427
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
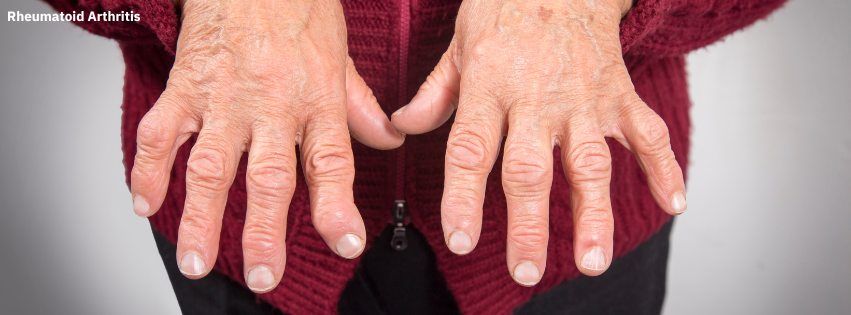
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints. It is an autoimmune disease, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, particularly the joints. This can lead to joint damage and deformities over time if not managed. RA commonly affects the small joints of the hands and feet but can also involve other body systems.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
RA symptoms usually develop gradually over time and can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Joint Pain: Painful joints, especially in the hands, feet and knees.
- Swelling: Inflamed joints causing swelling and tenderness.
- Stiffness: Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes, particulary after periods of inactivity.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness due to chronic inflammation.
- Loss of Appetite: Known as uveitis, which can cause eye pain and sensitivity to light.
- Rheumatoid Nodules: Firm lumps under the skin, usually around pressure points.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of RA is unknown, several risk factors can contribute to the development of the disease:
- Genetic Factors: Having family members with RA increases the risk.
- Gender: RA is more common in women than men.
- Age: Most cases are diagnosed between the ages of 40 and 60.
- Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for RA.
- Obesity: Being overweight may increase the likelihood of developing RA.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing RA involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and imaging techniques like X-rays or MRIs to detect joint damage. Doctors also test for specific markers like rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for RA, treatments are designed to reduce symptoms, slow down joint damage, and improve quality of life. Common treatments include:
- Medications Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and inflammation. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow disease progression. Biologic agents targeting the immune system in severe cases.
